Skin cancer is the most common type of cancer in the United States, with millions of cases diagnosed each year. Fortunately, many cases are preventable. You can significantly reduce your risk with a few proactive ways to prevent skin cancer.
Understanding skin cancer
There are primarily three types of skin cancer: basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma and melanoma. Each type has unique characteristics and risks, but they all share a common cause: exposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun and tanning beds.
Avoiding excessive sun exposure
Seek shade
One of the simplest ways to prevent skin cancer and protect your skin is to avoid direct sun exposure, especially during peak hours of 10 a.m. to 4 p.m. Find some shade under umbrellas, trees or shelters to minimize your UV radiation exposure.
Also, cloudy days don’t count as shade – UV rays can still travel through them and cause skin damage.
Wear protective clothing
Long-sleeved shirts, long pants, wide-brimmed hats and sunglasses hats provide effective protection against the sun’s rays. Clothing with a UV protection factor (UPF) rating offers additional defense. Sunglasses with UV protection can also prevent damage to your eyes and the delicate skin around them.
Using sunscreen properly
Choose the right sunscreen
Select a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30. Broad-spectrum sunscreens protect against both UVA and UVB rays. Look for products that are water-resistant if you plan to swim or sweat.
Apply generously and frequently
Apply sunscreen to all exposed skin 15 minutes before going outside. Use about one ounce (or the size of a shot glass) to cover your entire body. Reapply every two hours, or more often if swimming or sweating.
Avoiding tanning beds
Tanning beds emit UVA and UVB radiation, both of which increase the risk of skin cancer. The World Health Organization classifies tanning beds as a group 1 carcinogen, similar to tobacco. Opt for sunless tanning products if you desire a tanned appearance without the risks.
Regular skin examinations
Self-examinations
Performing regular self-examinations helps you identify any new or changing moles, spots or lesions. The “ABCDE rule” can help you remember what to look for:
- Asymmetry: One half of the mole does not match the other.
- Border: Irregular, scalloped or poorly defined edges.
- Color: Varying colors from one area to another.
- Diameter: Larger than 6mm (about the size of a pencil eraser).
- Evolving: Changes in size, shape or color.
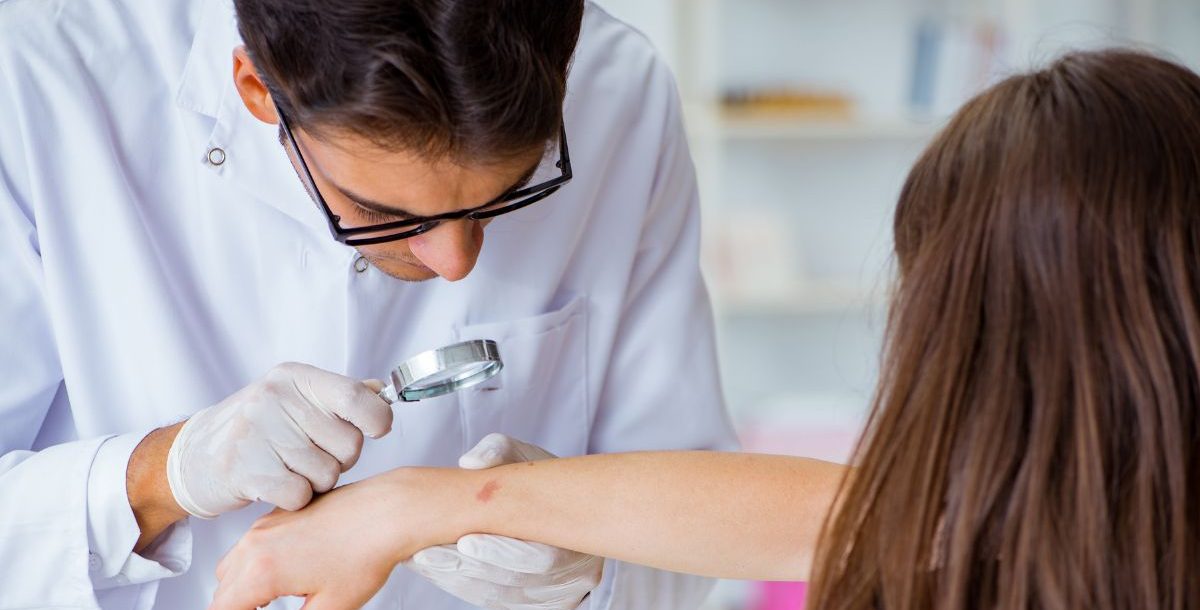
Professional skin exams
Visit a dermatologist annually for a professional skin examination, especially if you have a history of sunburns, a family history of skin cancer or numerous moles.
Protect children
Children are more sensitive to UV radiation. Infants younger than 6 months should be kept out of direct sunlight. For older children, apply sunscreen, dress them in protective clothing and encourage them to play in the shade.
Educate yourself and others
Awareness and education are crucial ways to prevent skin cancer. Stay informed about the latest research and guidelines and share this information with friends and family. Advocacy and community programs can also play a significant role in promoting skin health.
How we can help
Preventing skin cancer involves a combination of sun safety practices, regular skin examinations and a commitment to avoiding artificial sources of UV radiation. After wearing sunscreen, one of the best ways to prevent skin cancer includes seeing a dermatologist. Whether that’s to be proactive or because you have concerns, schedule an appointment for a skin exam with a dermatologist.
Learn about the dermatology services we offer at Bon Secours.